Kidney disease often goes unnoticed until it has progressed to a fairly advanced stage. However, recognizing early warning signs can help you receive timely treatment and prevent further complications. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll look at the different symptoms that may indicate kidney problems and what you can do to protect your kidney health.
Understanding Kidney Function
The kidneys are important organs that filter waste and excess water from the bloodstream, regulate blood pressure, and produce hormones that regulate red blood cell production. When kidneys are damaged, waste and fluids can accumulate in the body, causing a variety of health problems.
Early signs of kidney disease
Many early signs of kidney disease are subtle and can be easily overlooked or mistaken for other health conditions. It is important to be alert and seek medical advice if you experience any of the following symptoms:
1. Fatigue and lack of energy

Feeling constantly tired or having difficulty concentrating may be early signs of kidney disease. As the kidneys have difficulty filtering waste effectively, toxins can build up in the body, causing fatigue and lethargy.
2. sleep disorder

Chronic kidney disease (CKD) can disrupt sleep patterns, making you feel anxious and preventing you from getting a good night’s sleep. This can be caused by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances and complications related to kidney dysfunction.
3. Dry and itchy skin
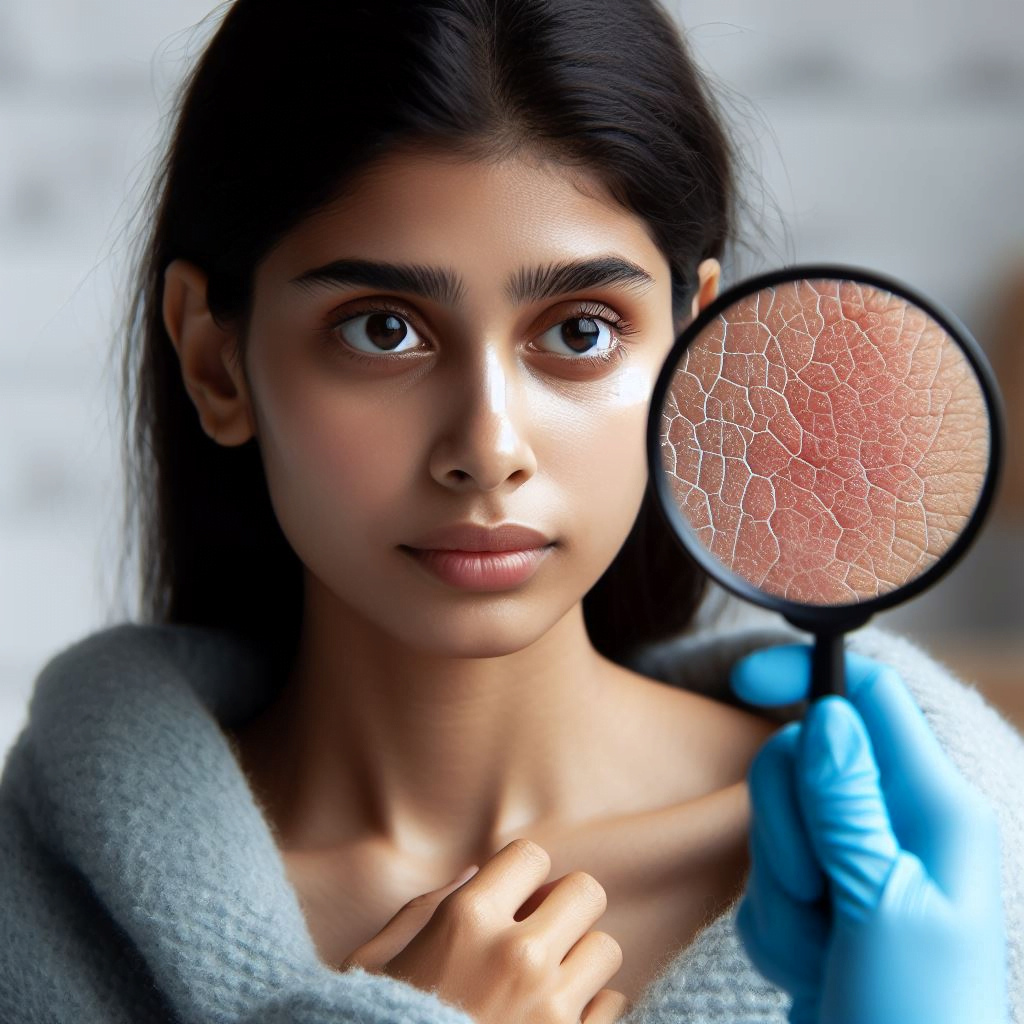

Healthy kidneys play an important role in maintaining the body’s fluid balance. If it is not functioning properly, fluid retention and accumulation of waste in the body can cause dry and itchy skin.
4. Nausea and vomiting

Reduced kidney function can cause toxins to build up in the bloodstream, causing nausea and vomiting, especially in the morning. This can also lead to loss of appetite and subsequent weight loss.
5. Muscle cramps and pain
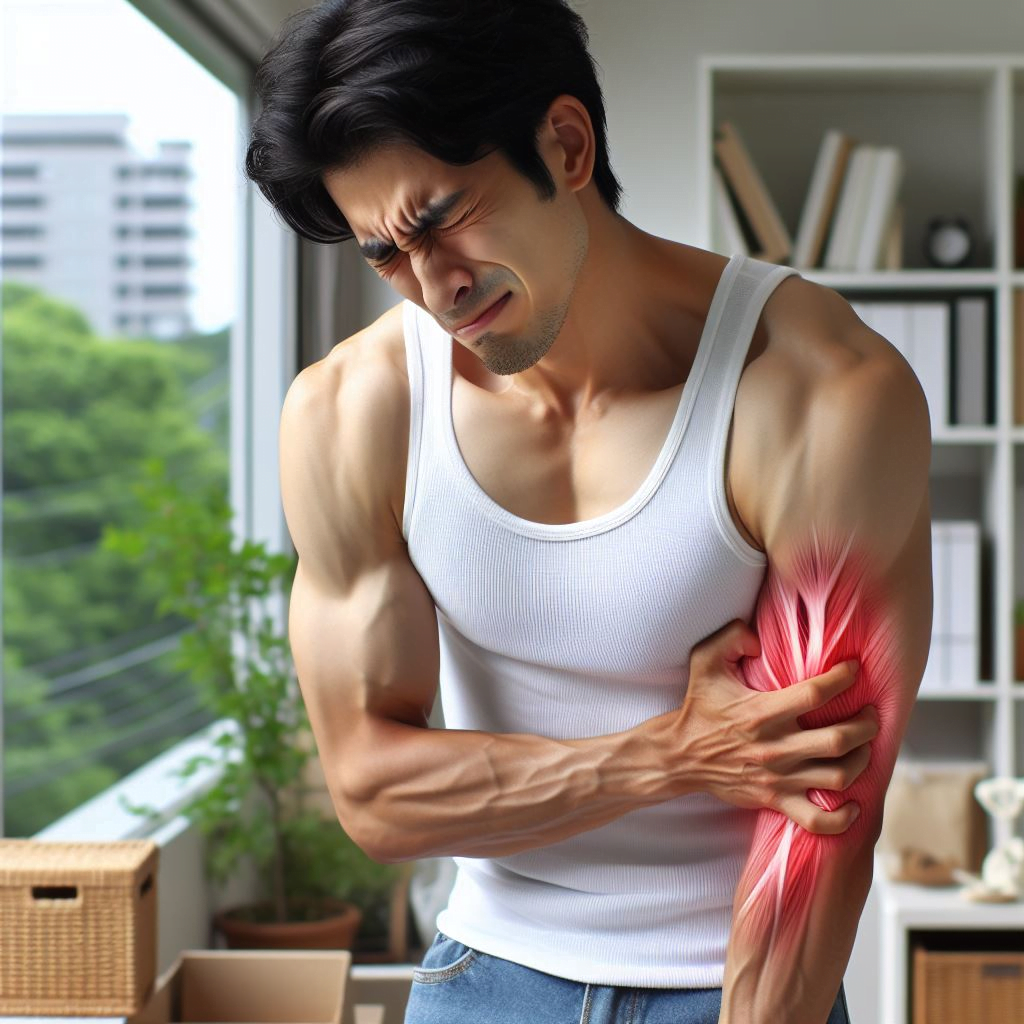

Electrolyte imbalance, a common result of kidney disease, can cause muscle cramps and pain. This discomfort can be felt in various parts of the body, including the legs, arms, and abdomen.
6. Swelling and water retention
Swollen ankles, feet, or hands may be a sign of fluid retention (edema) because the kidneys are unable to effectively remove excess fluid from the body.
7. Difficulty breathing

As kidney disease progresses, difficulty breathing may occur with minimal effort. This may be caused by fluid buildup in the lungs or the effects of anemia, which is common in people with kidney disease.
8. Changes in urination

Kidney disease can affect the frequency and appearance of urination. Blood or protein in the urine, frequent urination, or difficulty urinating may indicate a problem with kidney function.
9. High blood pressure

High blood pressure is both a cause and a symptom of kidney disease. Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage the kidneys over time, and kidney dysfunction can also lead to elevated blood pressure levels.
10. Diabetes risk

People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing kidney disease. If diabetes is not properly controlled, the small blood vessels in the kidneys can become damaged, resulting in a condition called diabetic nephropathy.
conclusion
By paying attention and recognizing the early signs of kidney disease, you can take proactive steps to protect your kidney health and prevent further complications. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to consult your healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis and treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can kidney disease be cured?
There is no cure for chronic kidney disease, but early detection and treatment can help slow the progression of the condition and prevent further complications. In some cases, treating the underlying cause, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, may improve kidney function.
Q2. What are the risk factors for kidney disease?
Important risk factors for kidney disease include diabetes, high blood pressure, family history, age (over 60 years), obesity, smoking, and certain medications or diseases.
Q3. How is kidney disease diagnosed?
Kidney disease is usually diagnosed using a combination of blood tests (to measure creatinine levels and estimated glomerular filtration rate), urine tests (to check for protein or blood), and imaging tests (such as ultrasound or CT scan).
