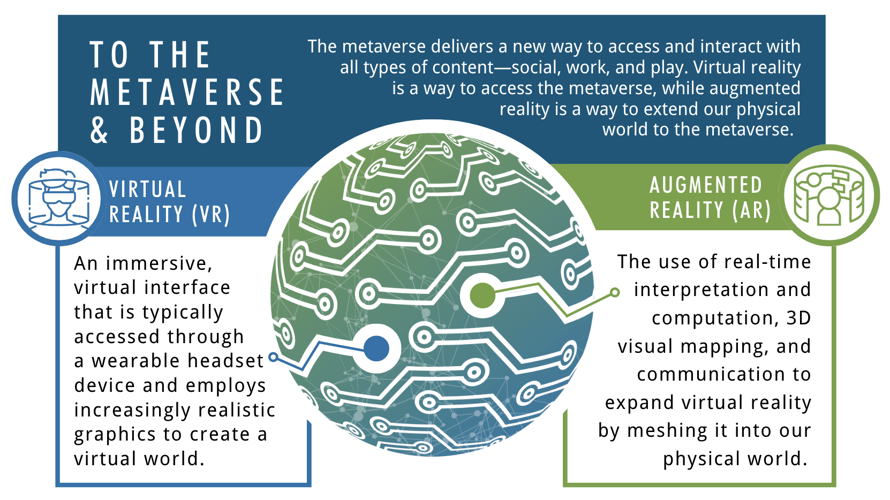
The gap between the digital and physical worlds is rapidly disappearing, ushering in a new era of immersive digital experiences. Immersive reality technologies use sensing technologies and spatial computing to help users “see the world differently” through mixed reality or augmented reality, or “see the world differently” through virtual reality.
These experiences will unfold across consumers, businesses, and industries. As the next logical step following the invention of mobile phones and PCs, virtual and augmented reality will enable the creation of entirely new business models, and some companies will quickly see their own “Kodak” moment. According to McKinsey, the world’s 2.7 billion deskless workers, or about 80% of the global workforce, are concentrated in eight industries, presenting enormous potential to scale immersive reality technologies.
 Venture capital investors provided approximately $4 billion in funding to AR/VR startups in 2021. This is guiding the development of new applications across many industries, which is expected to enable market growth of more than 20% per year, creating a $1 trillion base. Dollar market over the next 10-15 years. Technology barriers such as the need for longer battery life, lighter components, better ergonomics, and lack of maturity in the development process and supply chain have limited adoption, but recent advances are quickly shifting these challenges. past.
Venture capital investors provided approximately $4 billion in funding to AR/VR startups in 2021. This is guiding the development of new applications across many industries, which is expected to enable market growth of more than 20% per year, creating a $1 trillion base. Dollar market over the next 10-15 years. Technology barriers such as the need for longer battery life, lighter components, better ergonomics, and lack of maturity in the development process and supply chain have limited adoption, but recent advances are quickly shifting these challenges. past.
The technology ecosystem needed to support the Metaverse is vast, including many layers that have historically been underestimated by investors. These layers include a wide range of technologies, from data storage and computing power to connectivity and networking infrastructure, computer vision and sensors.
AR/VR development and infrastructure related companies
nvidia (Robo&THNQ:NVDA), Dassault (Robo & THNQ: DSY FP) and autodesk (ROBO & TTNQ: ADSK UK) is creating a unique approach to the digital world. We are using real-world simulations to reimagine product designs.
materialize (ROBO & HTEC: MTLS UW) and 3D Systems (ROBO & HTEC: DDD) is leading the development of virtual worlds that can be directly applied to real-world product production. Key applications include additive manufacturing. 3D bioprinting of organs, tissues, and musculoskeletal parts for implants; and testing new drugs.

Trimble (Robo: TRMB) And Faro Technologies (ROBO: FARO) brings virtual and augmented reality to construction and manufacturing processes. These solutions are already being used by operators around the world for manufacturing simulation.
Arista Networks (THNQ: ANET) and Pure Storage (THNQ: PSTG) is a leader in developing the large-scale cloud centers needed to run the metaverse. Storing this infinitely expanding data requires scalable solutions that enable fast and secure networking in cloud data centers.


